Enhanced tele-operation camera control by head motions
Sep 17, 2019Co-author:: Shang Gao, Ryosuke Tsumura, Jakub Kaminski, Loris Fichera, Haichong K Zhang
This work is published in SPIE Medical Imaging 2021. You can find out more information here
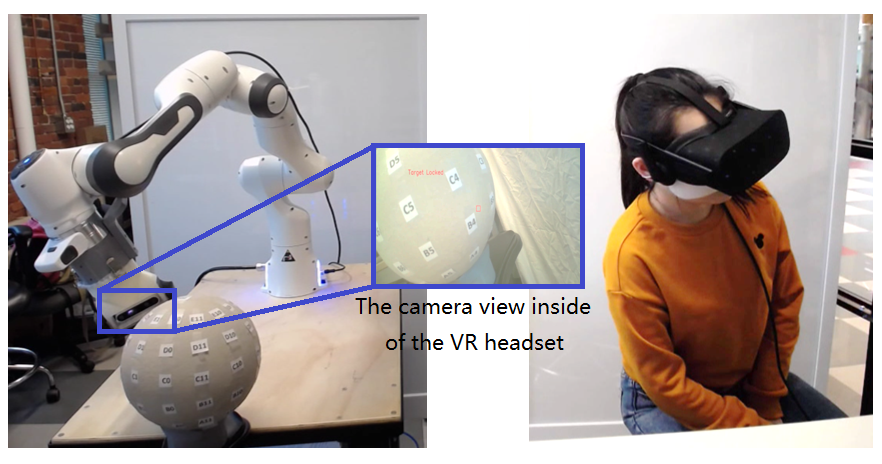
Traditional method that using head motion to control a remote camera maps the position and orientation directly or with scale factor. This is useful for a searching task, but not utilized for tasks such as examine an object.
We proposes a hands-free approach to control the camera view for an improved telepresence experience. The system comprises an RGBD camera mounted on a robotic arm and a motion tracking virtual reality (VR) head mount display (HMD) maps the human head and upper-body motion to the robotic arm for the immersive teleoperation task.
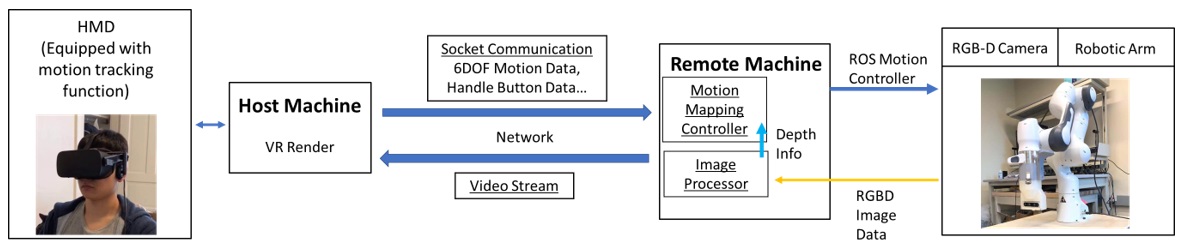
System block diagram
Based on this setup, an Augmented Head Motion Mapping (AHMM) mode is introduced. Wherein this mode, the user can decide to control the camera following the head motion directly or following the remote center of motion (RCM) to the target location so that the reachable visual field can be expanded.
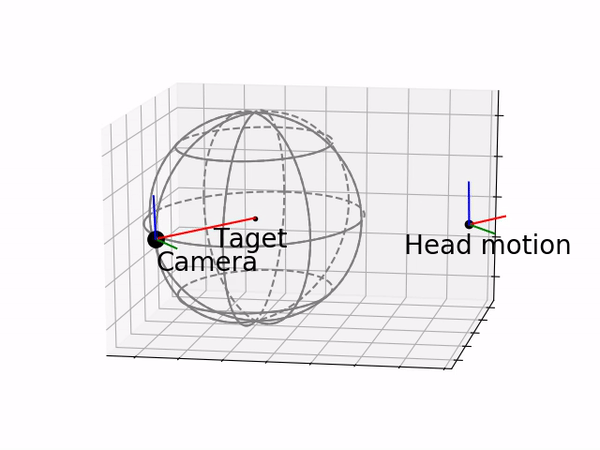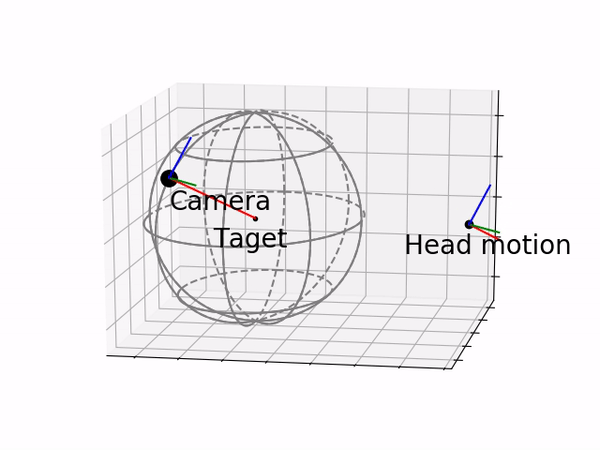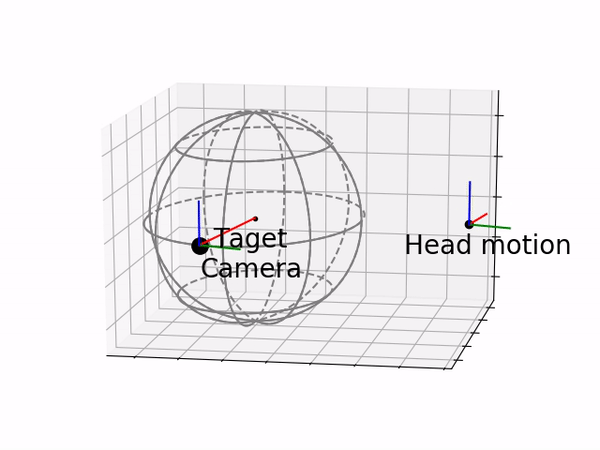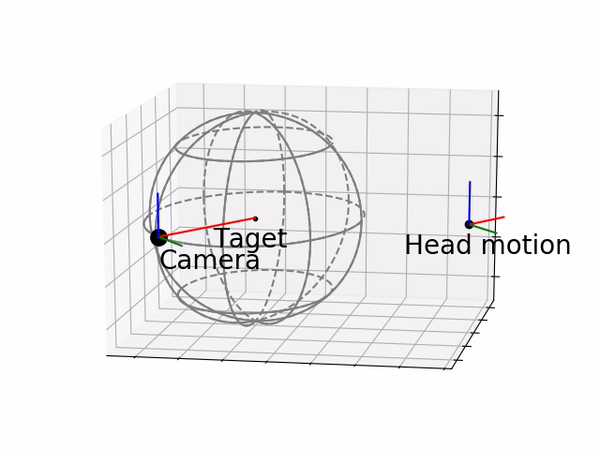
RCM mapping
We compared this AHMM with Direct Head Motion Mapping. A comparison demo can be found below:

The corresponding motion of the camera when the user performs
the same motion under different control mode.
Through the user study with seven subjects, we evaluated the proposed method compared with other conventional methods in terms of the reachable visual field, control intuitiveness, and task efficiency. The possibility of further enlarging the reachable visual field by introducing the motion scaling factor is investigated through the simulation. The result successfully demonstrated that an operator using the proposed system could examine a larger area on the given object within a similar amount of time with limited training.